June 12, 2024
In the first part of this perspective, I talked about the importance of a robust Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) strategy, and cited a number of compelling drivers behind adopting technological solutions to solve the challenges. In this one, the second in a series of three, we’ll take a deeper dive at one such technology that is transforming the Financial Services work: Artificial Intelligence (AI).
In North America, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into risk management programs by financial institutions is widespread and growing. According to a survey by NVIDIA, approximately 91% of financial services companies are either exploring AI or have already integrated it into their operations, including risk management.*
Specifically, more than 50% of the largest financial institutions in North America are using AI to enhance their risk management practices. These institutions are leveraging AI for various functions such as fraud detection, compliance monitoring, and climate risk assessments. AI technologies, including Generative AI and large language models (LLMs), are being employed to automate and streamline processes, thereby improving efficiency and effectiveness, as per a report by McKinsey.**
The adoption of AI in risk management is driven by the need to handle large volumes of data, enhance predictive capabilities, and comply with evolving regulatory requirements. Here are some other advantages of leveraging AI in GRC:
Leveraging AI-powered GRC: Key Advantages
Some of the key advantages of using AI in GRC were highlighted in the first part of this perspective. As a quick reminder, using AI in GRC involves techniques and tools can automatically find, ingest, and analyze vast amounts of regulatory data, identifying changes and possible conflicts before they become compliance headaches.
- Navigation Guide: A well-maintained GRC system operates as a navigational guide, helping chart your course through the regulatory frameworks. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns in past compliance issues, anticipate future risks, and suggest proactive strategies.
- Automating Compliance: Mundane compliance tasks can become incredibly time-consuming. AI automates repetitive processes like data collection, reporting, and even basic control assessments. This frees your team to concentrate on strategic initiatives and proactive risk management. Further, the prevalence and ease of adopting IoT helps integrate, contextualize and analyze data from multiple sources and formats, leading to automated analyses of vast and continuously available data in near real time.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Regulations are often complex and subjective and, hence, open to interpretation. AI can analyze your specific data to pinpoint areas where compliance might be unclear. AI can help provide immutable records and reliable proof points, empowering you to make informed choices with confidence and avoid unnecessary risks.
- Continuous Learning: The regulatory environment is constantly changing. But with AI, your GRC system becomes a self-learning entity. It can continuously monitor and automatically analyze new regulations and update your compliance framework, ensuring you’re always one step ahead.
However, embracing AI-powered GRC is not a one-time fix, and nor is AI a fix-all.
Key points to remember on your AI journey
- Data Quality is Essential: AI is only as good as the data it consumes. Ensure your GRC system has high-quality, reliable data to generate reliable insights.
- Human Expertise Remains Vital: AI is a powerful tool, but it cannot replace human judgment. Your team’s expertise is crucial for interpreting AI’s findings and making strategic decisions.
- Transparency Matters: As AI continues to play greater roles, be aware of how it approaches its conclusions; this builds trust and enhances your ability to utilize its abilities effectively.
Implementing AI has other challenges as well. Another example is in the areas of addressing integration and ethical biases, along with regulatory concerns in the use of AI and GRC technology solutions. These can be expanded to include:
- Data Integration: Integrating AI with GRC systems requires seamless data integration from various sources, often in different formats and structures.
- Ethical Biases: AI models can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in historical data, leading to unethical outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance: It is critical to ensure that AI systems follow the complex regulatory frameworks set by multiple financial regulatory bodies.
So, what are the solutions?
- Data Standardization: Implementing data standardization protocols across the organization to ensure uniformity in data processing.
- Bias Mitigation Techniques: Using advanced bias detection and mitigation algorithms to ensure fair and unbiased AI models.
- Regulatory Alignment: Developing a regulatory compliance framework that maps AI and GRC functionalities to specific requirements of each regulatory body.
AI use cases at leading US banks
1: JP Morgan Chase: Integration of AI in Fraud Detection
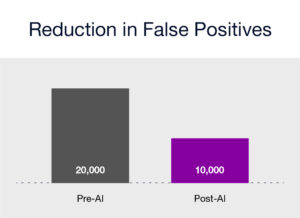
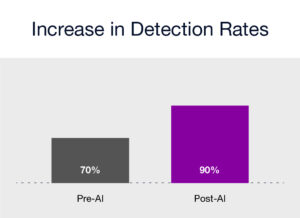
JP Morgan Chase, a leading financial institution, implemented AI-driven solutions for fraud detection. This initiative resulted in a 50% reduction in false positives coupled with a 30% increase in the detection rate of actual fraudulent activities. The success was attributed to the integration of heterogeneous data sources and the use of machine learning algorithms to find patterns indicative of fraud. This case study shows the potential of AI and GRC technologies in enhancing fraud detection capabilities, thereby improving operational efficiency, and reducing financial losses.
- Example 1: Reduction in False Positives (Pre-AI vs. Post-AI Implementation):
- Example 2: Increase in Detection Rates (Pre-AI vs. Post-AI Implementation):
- Example 3: JPMorgan Chase uses AI to monitor regulatory changes across 120,000 websites, significantly reducing the time spent on manual reviews.***
2: Wells Fargo Addressing Bias in Credit Scoring
Wells Fargo used AI to refine its credit scoring models. By incorporating bias mitigation techniques, they reduced racial bias in loan approval rates by 25%, ensuring a fairer credit evaluation process1.
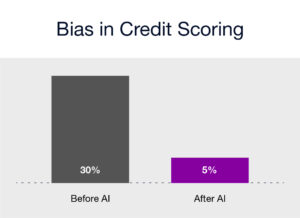
- Before: 30% discrepancy between racial groups
- After: 5% discrepancy between racial groups.****
Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
AI’s use in GRC is instrumental in ensuring compliance with both current and future AI regulations through its proactive approach.
By incorporating AI practices with regulatory standards, organizations can avoid legal repercussions, reputational harm, and financial losses. Additionally, AI’s use fosters responsible AI innovation by promoting ethical AI development, ensuring transparency in AI decision-making, and encouraging continuous monitoring and improvement. This empowers organizations to innovate while maintaining compliance and safeguarding public interests.
This requires a multi-faceted approach, involving the development of robust frameworks, using technology, and adhering to stringent regulatory standards set up by entities such as the OCC, SEC, FRB, FINRA, FDIC, OFAC, and FinCEN.
The figure below shows a regulatory framework alignment, summarizing how the use of AI in GRC has improved significantly in recent years. There is a considerable enhancement in a program’s effectiveness and a substantial reduction in the requirement for manual rework:

Figure 1: Regulatory Framework Alignment
Future Trends and Considerations
Regulatory Sandboxes
Fortunately, regulatory sandboxes, a tool for financial institutions, provide a safe environment to test AI innovations under the watchful eye of regulators. This controlled environment allows institutions to fine-tune their AI systems, ensuring compliance and minimizing risks before full-scale deployment.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Ongoing monitoring and auditing of AI systems are crucial to ensure their continued compliance and effectiveness. Given the potential risks and challenges associated with AI systems, such as privacy, security, bias, transparency model, third party risks, etc., financial institutions must establish robust monitoring frameworks to detect and address any issues promptly.
Collaboration with Regulators
Collaboration between financial institutions and regulators is essential to address the challenges posed by AI. This collaboration can provide financial institutions with early access to regulatory changes, enabling them to adapt their AI systems in a timely manner. Regular dialogue can also help align AI development with regulatory expectations and foster a more supportive regulatory environment.
Evolving Regulatory Frameworks
As AI technology evolves, so will regulatory frameworks. Financial institutions must stay abreast of regulatory developments and be prepared to adapt their AI systems to comply with new requirements.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in GRC technologies, while addressing ethical biases and regulatory concerns, is underpinned by the need for a structured approach. This includes the use of advanced data integration techniques, bias mitigation algorithms, and stringent adherence to regulatory standards. By aligning AI applications with regulatory requirements, financial institutions can enhance operational efficiency, ensure ethical standards, and support compliance with regulatory bodies, thereby instilling confidence in the ethical and legal aspects of AI and GRC integration.
Stay tuned with us for the next expert perspective in this series coming next week, on Cyber Resilience.
Sources: NVIDIA Survey, 2024
** A report by McKinsey and Company, 2024
***News published by American Banker, 2023
****Article published by Risk.net, 2021.
By Joshua Wick, Global Head of Risk and Compliance, Hitachi Digital Services










